Explain the Difference Between Exons and Introns
Introns are removed via RNA splicing and exons are joined together to form coding. Differences between Exons and Introns.

Difference Between Introns And Exons Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms
Genes in the genome consist of exons and introns.
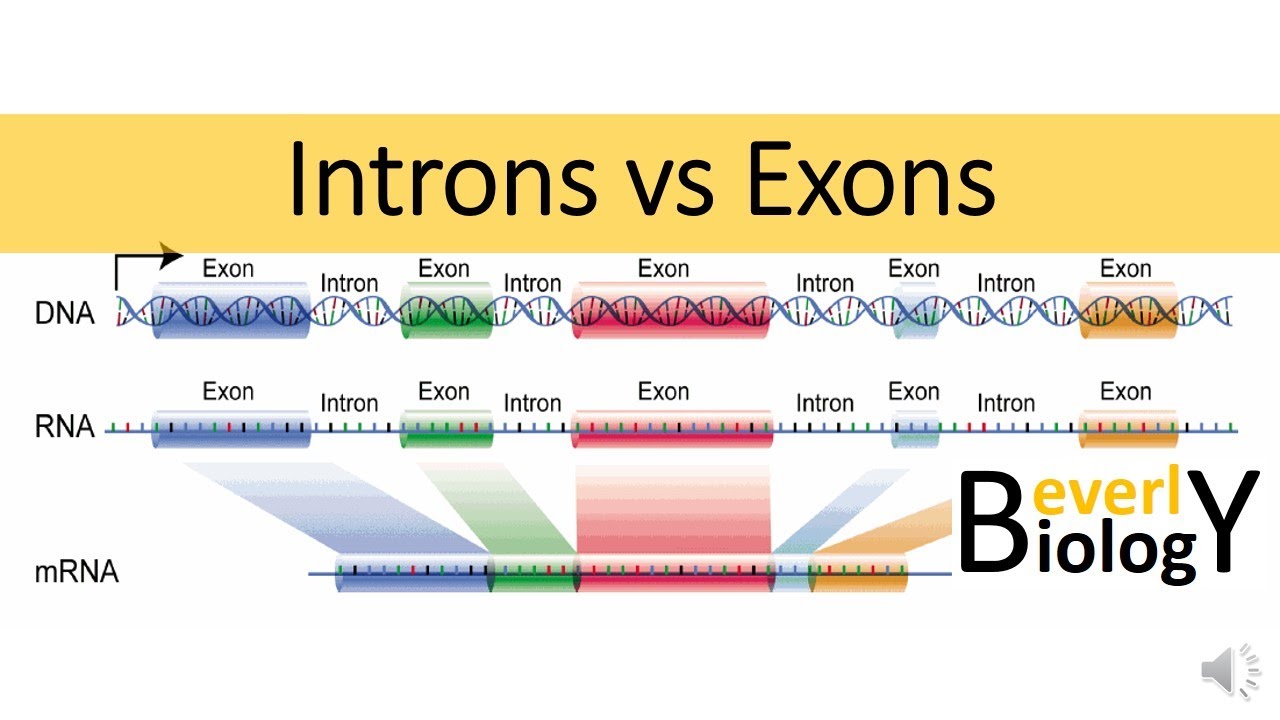
. Exons are coding areas whereas introns are non-coding areas. One of the fundamental issues in RNA splicing research is represented by understanding how the spliceosome can successfully define exons and introns in a huge variety of pre-mRNA molecules with nucleotide-precision. Intons can be termed as DNA bases that are found between Exons.
Some exons are coding in that they contain information for making a protein whereas others are non-coding. Exons are coding areas that have code for protein whereas introns are non-coding areas that are not at all implicated with the protein coding. Exons are converted into messenger RNA to allow these parts of the gene to then be transcribed into protein.
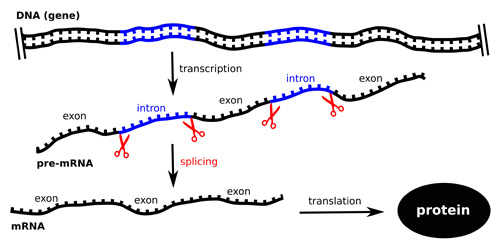
Introns are the. Introns on the other hand are termed as nucleotide sequences seen within the genes which are removed through RNA splicing for generating a mature RNA molecule. 7 rows Exons are termed as nucleic acid coding sequences which are present in mRNA.
An intron refers to non-coding sequences found in DNA or RNA. 1 exons are the coding areas whereas introns are the non coding areas of the gene. Introns and exons are parts of genes.
Exons code for proteins whereas introns do not. In a self splitting intron the hairpin structure brings the ends o the introns near to the branch point. Differences between Exons and Introns.
Exons are said to be those sequences that appear in mature or processed RNA. Exon shuffling - early genes were probably very small and so were peptides - the peptides agrregated together to make proteins-non-coding regions became introns and mechanisms evolved for self splicing. 13 rows Exons are protein-coding DNA sequences that require the necessary codons or information necessary.
An exon is termed as a nucleic acid sequence which is represented in the RNA molecule. An exon is a region of the genome that ends up within an mRNA molecule. 2 exons code for the proteins but the introns are not implicated with the protein coding.
Three common technical terms in molecular genetics exon intron and codon have specific technical definitions but are often miss-used in hurried or short-hand presentations. 8 rows Introns are the transcribed part of the nucleotide sequence in an mRNA and bound to carry the. Introns or the intervening sequence are considered as the non-coding part of the genes while the exons or the expresses sequence are known to be as the coding part for proteins of the genes.
The difference between self-splicing intron and one which requires the spliceosome is that the non-self splicing introns can split any introns almost any size. Introns are the common attribute found in the genes of the multicellular eukaryotes like humans while exons are found in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Introns and exons are parts of genes - exons code for proteins whereas introns do not ie.
Process by which the DNA sequences encoding exons are exchanged and reordered through genetic recombination between DNA sequences encoding introns. But in several cases the potential was equally apparent in exons and introns Forsdyke 1995a. But the essential difference between the two is that one is made into protein and the other is not.
A great way to remember this is by considering introns as intervening sequences and exons as expressed sequences. Introns are non protein coding regions and are removed in a process termed splicing by snRNPs. Group of answer choices aRNA editing bExon Definition c Exon Shuffling dTransesterification.
- introns may be vital in not only terms of right now but their origins - presence of introns may be important in how genes evolved. 1 exons are the coding areas whereas introns are the non coding areas of the gene. Exons refer to the coding portions of DNA or RNA.
Introns and Exons are the genetic material. The average of the 13 differences between each peptide-binding. The main thing to remember is that exon and introns are features of DNA whereas codons are features of RNA.
Most eukaryotic genes splits into two alternative repeating parts ie Exons Coding Regionand Introns non coding regions. Then the introns themselves catalyze the making of the loop joining the two exons. An explanation of introns in these terms needs to explain why introns interrupt message sequences and why the sequence of an intron is so different from the exons surrounding it.
Since its first description researchers in this field have identified and characterized many fundamental elements and. An exon is a sequence of nucleic acids that are represented in the m RNA molecule whereas introns are not expressed into into m RNA. Homologous sequences in the other type of nucleic need to be called something else.
2 exons code for the proteins but the introns are not implicated with the protein coding. Answered by David B. Because Introns are non-coding.
Introns Vs Exons Definition 12 Major Differences Examples
Difference Between Introns And Exons Definition Characteristics Function Comparison
What Is The Difference Between An Intron And An Exon Socratic
No comments for "Explain the Difference Between Exons and Introns"
Post a Comment